This blog post explains how to access Identity Server 2.0 Security Token Service [STS] programmatically.
First you need to configure the Identity Server STS to issue security tokens.
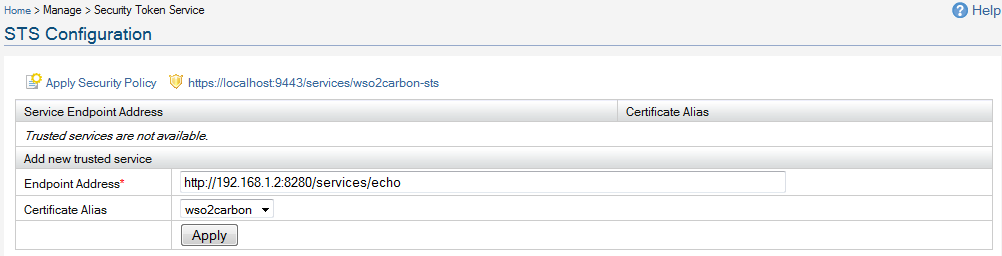
Login as admin/admin to the management console and access 'Security Token Service'.
There you need to enter the relying parties you trust - in other words, which relying parties who will accept security tokens from the Identity Server.
You need to upload the public certificate of the trusted relying party - against it's end point.
When issuing tokens - it'll be encrypted from the public key of the trusted relying party.
So - even the client who obtains the token to send to the RP - has no visibility to the included token.
Now - let's apply security to the STS - here we provide UsernameToken based security - that means, to obtain a token from the STS, the client should have a valid user account with the Identity Server.
Click on the 'Apply Security Policy' link to configure security and go through the wizard.
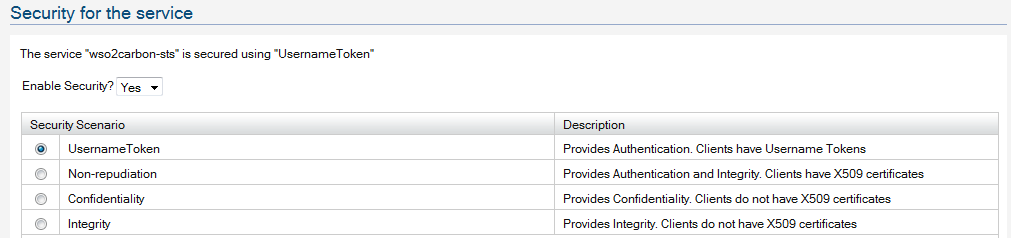
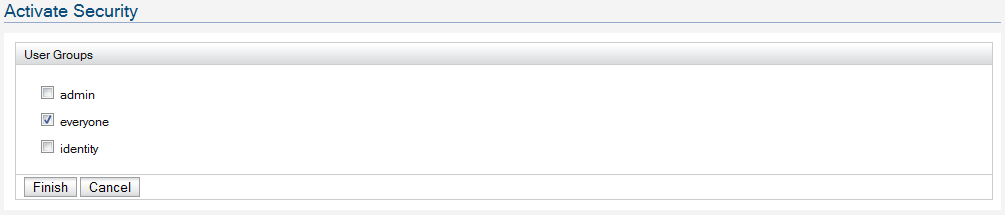
That's it and that's all we need to configure Identity Server STS to issue security tokens.
Let's focus on the client code.
package org.apache.ws.axis2;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMAbstractFactory;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMElement;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMFactory;
import org.apache.axiom.om.impl.builder.StAXOMBuilder;
import org.apache.axis2.context.ConfigurationContext;
import org.apache.axis2.context.ConfigurationContextFactory;
import org.apache.neethi.Policy;
import org.apache.neethi.PolicyEngine;
import org.apache.rahas.RahasConstants;
import org.apache.rahas.Token;
import org.apache.rahas.TrustUtil;
import org.apache.rahas.client.STSClient;
import org.apache.rampart.policy.model.RampartConfig;
import org.apache.ws.secpolicy.Constants;
import org.opensaml.XML;
public class IdentitySTSClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
final static String RELYING_PARTY_SERVICE_EPR = "http://192.168.1.2:8280/services/echo";
final static String STS_EPR = "https://localhost:9443/services/wso2carbon-sts";
/**
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConfigurationContext confContext = null;
Policy stsPolicy = null;
STSClient stsClient = null;
Policy servicePolicy = null;
Token responseToken = null;
String trustStore = null;
// You need to import the Identity Server, public certificate to this key store.
trustStore = "clientkeystore.jks";
// We are accessing STS over HTTPS - so need to set trustStore parameters.
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStore", trustStore);
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword", "wso2carbon");
// Create configuration context - you will have Rampart module engaged in the client.axis2.xml
confContext = ConfigurationContextFactory.createConfigurationContextFromFileSystem("repo","repo/conf/client.axis2.xml");
stsClient = new STSClient(confContext);
stsClient.setRstTemplate(getRSTTemplate());
stsClient.setAction(RahasConstants.WST_NS_05_02 + RahasConstants.RST_ACTION_SCT);
// This is the security policy we applied to Identity Server STS.
// You can see it by https://[IDENTITY_SERVER]/services/wso2carbon-sts?wsdl
stsPolicy = loadPolicy("sts.policy.xml");
// This is the security of the relying party web service.
// This policy will accept a security token issued from Identity Server STS
servicePolicy = loadPolicy("service.policy.xml");
responseToken = stsClient.requestSecurityToken(servicePolicy, STS_EPR, stsPolicy, RELYING_PARTY_SERVICE_EPR);
System.out.println(responseToken.getToken());
}
private static Policy loadPolicy(String xmlPath) throws Exception {
StAXOMBuilder builder = null;
Policy policy = null;
RampartConfig rc = null;
builder = new StAXOMBuilder(xmlPath);
policy = PolicyEngine.getPolicy(builder.getDocumentElement());
rc = new RampartConfig();
rc.setUser("admin");
// You need to have password call-back class to provide the user password
rc.setPwCbClass(PWCBHandler.class.getName());
policy.addAssertion(rc);
return policy;
}
private static OMElement getRSTTemplate() throws Exception {
OMFactory fac = OMAbstractFactory.getOMFactory();
OMElement elem = fac.createOMElement(Constants.RST_TEMPLATE);
TrustUtil.createTokenTypeElement(RahasConstants.VERSION_05_02, elem).setText(XML.SAML_NS);
TrustUtil.createKeyTypeElement(RahasConstants.VERSION_05_02, elem,
RahasConstants.KEY_TYPE_SYMM_KEY);
TrustUtil.createKeySizeElement(RahasConstants.VERSION_05_02, elem, 256);
return elem;
}
}